NASA is locating ice on Mars with this new map
by Staff Writers
Pasadena CA (JPL) Oct 30, 2023
Buried ice will be a vital resource for the first people to set foot on Mars, serving as drinking water and a key ingredient for rocket fuel. But it would also be a major scientific target: Astronauts or robots could one day drill ice cores much as scientists do on Earth, uncovering the climate history of Mars and exploring potential habitats (past or present) for microbial life.
The need to look for subsurface ice arises because liquid water isn’t stable on the Martian surface: The atmosphere is so thin that water immediately vaporizes. There’s plenty of ice at the Martian poles – mostly made of water, although carbon dioxide, or dry ice, can be found as well – but those regions are too cold for astronauts (or robots) to survive for long.
That’s where the NASA-funded Subsurface Water Ice Mapping project comes in. SWIM, as it’s known, recently released its fourth set of maps – the most detailed since the project began in 2017.
Led by the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, SWIM pulls together data from several NASA missions, including the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), 2001 Mars Odyssey, and the now-inactive Mars Global Surveyor. Using a mix of data sets, scientists have identified the likeliest places to find Martian ice that could be accessed from the surface by future missions.
Instruments on these spacecraft have detected what look like masses of subsurface frozen water along Mars’ mid-latitudes. The northern mid-latitudes are especially attractive because they have a thicker atmosphere than most other regions on the planet, making it easier to slow a descending spacecraft. The ideal astronaut landing sites would be a sweet spot at the southernmost edge of this region – far enough north for ice to be present but close enough to the equator to ensure the warmest possible temperatures for astronauts in an icy region.
“If you send humans to Mars, you want to get them as close to the equator as you can,” said Sydney Do, JPL’s SWIM project manager. “The less energy you have to expend on keeping astronauts and their supporting equipment warm, the more you have for other things they’ll need.”
Building a Better Map
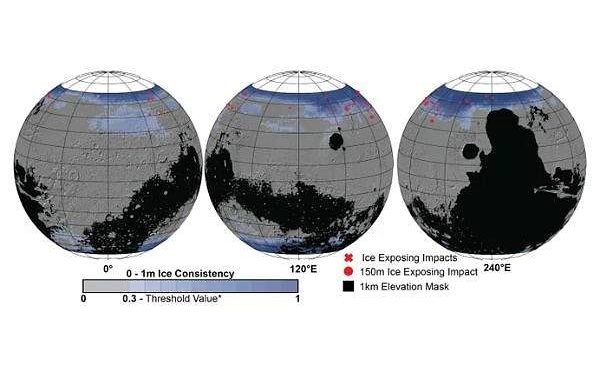
Previous iterations of the map relied on lower-resolution imagers, radar, thermal mappers, and spectrometers, all of which can hint at buried ice but can’t outright confirm its presence or quantity. For this latest SWIM map, scientists relied on two higher-resolution cameras aboard MRO. Context Camera data was used to further refine the northern hemisphere maps and, for the first time, HiRISE (High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) data was incorporated to provide the most detailed perspective of the ice’s boundary line as close to the equator as possible.
Scientists routinely use HiRISE to study fresh impact craters caused by meteoroids that may have excavated chunks of ice. Most of these craters are no more than 33 feet (10 meters) in diameter, although in 2022 HiRISE captured a 492-foot-wide (150-meter-wide) impact crater that revealed a motherlode of ice that had been hiding beneath the surface.
“These ice-revealing impacts provide a valuable form of ground truth in that they show us locations where the presence of ground ice is unequivocal,” said Gareth Morgan, SWIM’s co-lead at the Planetary Science Institute. “We can then use these locations to test that our mapping methods are sound.”
In addition to ice-exposing impacts, the new map includes sightings by HiRISE of so-called “polygon terrain,” where the seasonal expansion and contraction of subsurface ice causes the ground to form polygonal cracks. Seeing these polygons extending around fresh, ice-filled impact craters is yet another indication that there’s more ice hidden beneath the surface at these locations.
There are other mysteries that scientists can use the map to study, as well.
“The amount of water ice found in locations across the Martian mid-latitudes isn’t uniform; some regions seem to have more than others, and no one really knows why,” said Nathaniel Putzig, SWIM’s other co-lead at the Planetary Science Institute. “The newest SWIM map could lead to new hypotheses for why these variations happen.” He added that it could also help scientists tweak models of how the ancient Martian climate evolved over time, leaving larger amounts of ice deposited in some regions and lesser amounts in others.
SWIM’s scientists hope the project will serve as a foundation for a proposed Mars Ice Mapper mission – an orbiter that would be equipped with a powerful radar custom-designed to search for near-surface ice beyond where HiRISE has confirmed its presence.
Related Links
Mars Water Resource Maps
Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com
Lunar Dreams and more