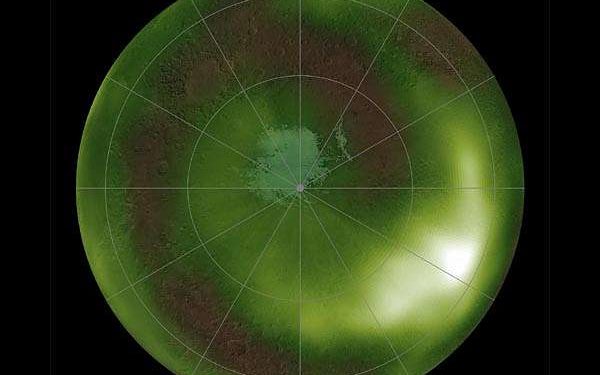
A green glow in the Martian night
by Staff Writers
Paris (ESA) Nov 13, 2023
When future astronauts explore Mars’s polar regions, they will see a green glow lighting up the night sky. For the first time, a visible nightglow has been detected in the martian atmosphere by ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) mission.
Under clear skies, the glow could be bright enough for humans to see by and for rovers to navigate in the dark nights. Nightglow is also observed on Earth. On Mars it was something expected, yet never observed in visible light until now.
Light the way
The atmospheric nightglow occurs when two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule, about 50 km above the planetary surface.
The oxygen atoms have been on a journey: they form on Mars’s dayside when sunlight gives energy to carbon dioxide molecules, making them split apart. When the oxygen atoms migrate to the night side and stop being excited by the Sun, they regroup and emit light at lower altitudes.
“This emission is due to the recombination of oxygen atoms created in the summer atmosphere and transported by winds to high winter latitudes, at altitudes of 40 to 60 km in the martian atmosphere,” explains Lauriane Soret, researcher from the Laboratory of Atmospheric and Planetary Physics of the University of Liege, in Belgium, and part of the team that published the discovery in Nature Astronomy.
The illumination from the nightglow could be bright enough to light the way of future see the glow as bright as moonlit clouds on Earth.
“These observations are unexpected and interesting for future trips to the Red Planet,” says Jean-Claude Gerard, lead author of the new study and planetary scientist at the University of Liege.
Follow the green glowing road
wThe international scientific team was intrigued by a previous discovery made using Mars Express, which observed the nightglow in infrared wavelengths a decade ago. The Trace Gas Orbiter followed up by detecting glowing green oxygen atoms high above the dayside of Mars in 2020 – the first time that this dayglow emission was seen around a planet other than Earth.
These atoms also travel to the nightside and then recombine at lower altitude, resulting in the visible nightglow detected in the newly published research.
Orbiting the Red Planet at an altitude of 400 km, TGO was able to monitor the night side of Mars with the ultraviolet-visible channel of its NOMAD instrument. The instrument covers a spectral range from near ultraviolet to red light and was oriented towards the edge of the Red Planet to better observe the upper atmosphere.
The NOMAD experiment is led by the Royal Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy, working with teams from Spain (IAA-CSIC), Italy (INAF-IAPS), and the United Kingdom (Open University), among others.
Scientific value
The nightglow serves as a tracer of atmospheric processes. It can provide a wealth of information about the composition and dynamics of a region of the atmosphere difficult to measure, as well as the oxygen density. It can also reveal how energy is deposited by both the Sun’s light and the solar wind – the stream of charged particles emanating from our star.
Understanding the properties of Mars’ atmosphere is not only scientifically interesting but it is also key for missions to the Red Planet’s surface. Atmospheric density, for example, directly affects the drag experienced by orbiting satellites and by the parachutes used to deliver probes to the martian surface.
Nightglow versus aurora
Nightglow is also observed on Earth, but it is not to be confused with auroras. Auroras are just one way in which planetary atmospheres light up.
Auroras are produced, on Mars as on Earth, when energetic electrons from the Sun hit the upper atmosphere. They vary across space and time, while nightglow is more homogeneous. Nightglow and auroras can both exhibit a wide range of colours depending on which atmospheric gases are most abundant at different altitudes.
The green nightglow on our planet is quite faint, and so is best seen by looking from an ‘edge on’ perspective – as portrayed in many spectacular images taken by astronauts from the International Space Station.
Related Links
Human and Robotic Exploration at ESA
Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com
Lunar Dreams and more