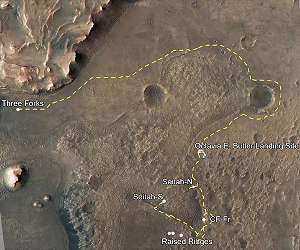
Since February 18, 2021, Perseverance has been exploring the Jezero crater floor, including an exposure of rock and sand that the rover’s science team calls Seitah (which means “amongst the sand” in the Navajo language).
One of the main exploration targets within Jezero crater is the well-preserved delta deposit, and many of the predicted landing sites for the rover were clustered very near the scarp of this delta. However, during landing, the rover’s computer diverted the rover away from the delta to the eastern side of Seitah, which itself was considered too sandy and rocky for a safe landing.
While the rover’s detailed exploration of the Jezero delta will have to wait until later in the mission, the rover’s landing site has given the team an opportunity to dig into the geology and origin of the crater floor rock units.
During the first few months of the mission, Perseverance explored a heavily cratered rock unit containing abundant polygonal fractures and a composition similar to a basaltic volcanic rock. In September 2021, Perseverance entered Seitah and began exploring a new and different geologic unit. The rocks in Seitah have a very interesting composition, and are mostly comprised of the mineral olivine.
The rocks of Seitah also appear very similar to a geological unit that covers nearly 20,000 km2 outside of Jezero crater. Olivine is an igneous mineral, and is typically one of the first minerals to crystallize out of a magma. Scientists on the rover team are trying to understand how this olivine-rich rock could have formed. One of the ways we do this is by identifying “terrestrial analogues,” or rocks here on Earth that look similar to what the rover is seeing on Mars.
One possibility could be ancient (3.5 billion year old) lava flows emplaced in Western Australia, close to the earliest good evidence of life here on Earth is preserved. The evidence of life is preserved in microbial mounds called “stromatolites”.
Igneous rocks, like these Australian lava flows, can be easily dated and can provide important age constraints on the timing of geologic processes and conditions and provide context for any biologically mediated rocks that might be present. The olivine-bearing rocks of Seitah could provide important context and constraints on the timing of the Jezero crater lake.
As the rover wraps up its exploration of the crater floor, excitement is building for the next phase of the mission: the Jezero delta. Will we find evidence of ancient martian life on the delta? Stay tuned.
Related Links
Perseverance Mars 2020
Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com
Lunar Dreams and more
|
We need your help. The SpaceDaily news network continues to grow but revenues have never been harder to maintain. With the rise of Ad Blockers, and Facebook – our traditional revenue sources via quality network advertising continues to decline. And unlike so many other news sites, we don’t have a paywall – with those annoying usernames and passwords. Our news coverage takes time and effort to publish 365 days a year. If you find our news sites informative and useful then please consider becoming a regular supporter or for now make a one off contribution. |
||
|
SpaceDaily Contributor $5 Billed Once credit card or paypal |
SpaceDaily Monthly Supporter $5 Billed Monthly paypal only |
|
![]()
To Seitah and Back
Pasadena CA (JPL) Dec 17, 2021
Six months ago, we began the dedicated investigation of the Jezero crater floor, and now in December 2021 we are more than halfway through this first science campaign. Since our first sampling experience at Roubion and our first sample pair from the Rochette rock, we have collected a second sample pair, this time from a region of the crater floor called Seitah at the Brac rock. As we now gear up to acquire our next, and third, sample pair, in Seitah, we can take a look back at the steps that brought Per … read more