Organic molecules on Mars linked to atmospheric formaldehyde
by Riko Seibo
Tokyo, Japan (SPX) Sep 20, 2024
Mars, now a cold and dry planet, once had liquid water, which raises the possibility of ancient life. In pursuit of this idea, researchers at Tohoku University developed a model showing how organic matter could have formed in Mars’ ancient atmosphere.
Organic matter, which can originate from living organisms or chemical processes, contains carbon isotopes that give clues about its formation. NASA’s Curiosity rover previously found Martian sediment samples unusually depleted in the carbon isotope 13C, but the reasons behind this were unclear.
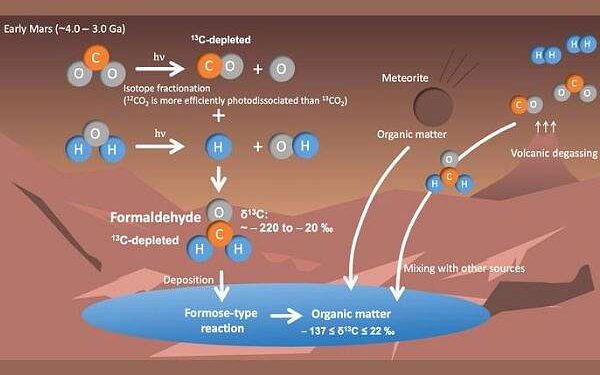
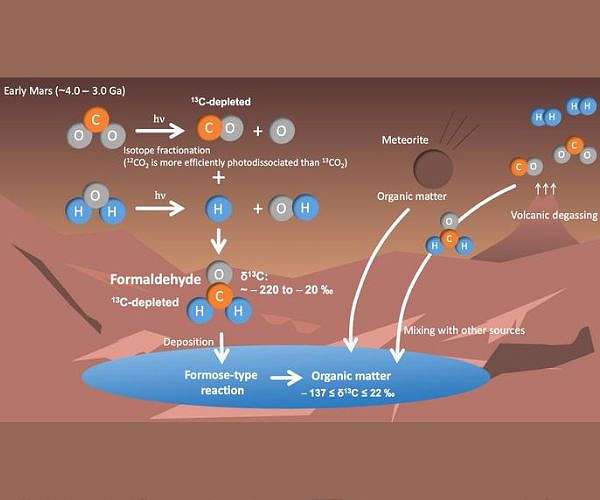
Led by Shungo Koyama, Tatsuya Yoshida, and Naoki Terada, the Tohoku University team explored the role of formaldehyde (H2CO) in Mars’ atmospheric history. Their model suggests that formaldehyde, produced in the planet’s atmosphere billions of years ago, may explain the curious 13C depletion observed by the rover. Formaldehyde is key to forming complex organic compounds like sugars, which are essential to life.
The team’s model used a combination of photochemical and climate models to estimate how the carbon isotope ratio of formaldehyde changed on Mars over 3 to 4 billion years. They found that the depletion of 13C resulted from the photodissociation of CO2 by ultraviolet sunlight. The model also showed that factors like atmospheric pressure, volcanic hydrogen emissions, and the planet’s CO-to-CO2 ratio influenced the variations in carbon isotope ratios.
“This model provides a possible explanation for previously unexplained findings, such as why 13C was mysteriously depleted,” Koyama, a graduate student at Tohoku University, remarked.
These findings suggest that formaldehyde might have played a crucial role in producing bio-important molecules, such as sugars and ribose (an RNA component), on ancient Mars.
Research Report:Stable carbon isotope evolution of formaldehyde on early Mars
Related Links
Tohoku University
Mars News and Information at MarsDaily.com
Lunar Dreams and more