A few hours after darkness falls during November, the unquestioned landmark of the autumn night sky occupies a commanding position high in the south: the flying horse Pegasus.
The horse’s body is formed by four bright stars — the famous Great Square — one of the easiest star patterns for astronomy neophytes to trace out. The Great Square is also a good starting point to become acquainted with the colors of the stars. Alpheratz, the top left star of the square, is white, but Scheat at top right is distinctly reddish. The difference is perhaps most easily seen by repeatedly looking at one star for several seconds and then the other.
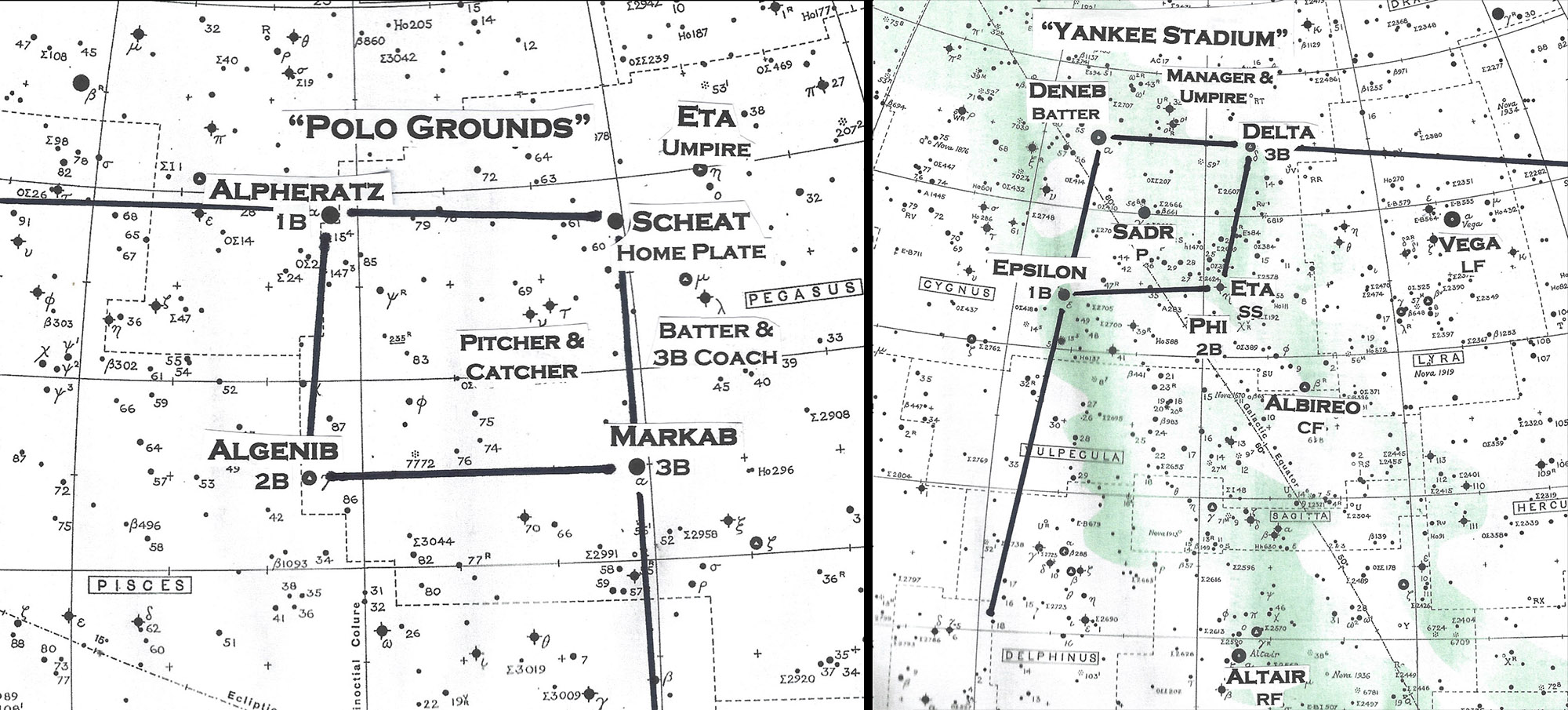
Play ball!
Pegasus was a constellation that I had great fun pointing out to audiences at New York’s Hayden Planetarium. From the Great Square of Pegasus, I’d map out a celestial baseball game in the sky. The star Scheat marked home plate; Alpheratz, first base; Algenib second; and Markab third.
I’d then create various plays, utilizing stars from adjacent constellations in Aries, Pisces, Cetus, Aquarius, and Piscis Austrinus as outfielders. In the last constellation, I used the bright star Fomalhaut as the left fielder, with his back up against the foul pole chasing after a home run ball already in the stands. Incidentally, the two stars that mark the western (right) side of the Great Square point almost exactly toward Fomalhaut.
Actually, this is one of two baseball games now well-placed in our mid-autumn sky. We can also incorporate the Summer Triangle, which is still well placed high in the west. That other baseball diamond was conceived by astronomer Henry Neely (1879-1963), who worked at Hayden Planetarium during the 1950s and who was known as the “Dean of New York Stargazers.” Neeley outlined it in his 1946 book “A Primer for Star Gazers” (Harper & Brothers), a dated but still excellent guide to the constellations, copies of which can still be found online.
Five years ago, I wrote a Space.com column comparing Neeley’s baseball diamond to the one in Pegasus. I referred to Neeley’s as Yankee Stadium, while the “Great Square baseball diamond” was the Polo Grounds.
Incidentally, if we go back to Pegasus: For the pitcher, I utilized a dim 4 h-magnitude star, Upsilon Pegasi, seemingly having a conversation with a star of similar brightness (Tau), which could be the catcher. The moderately bright star Matar could represent the home plate umpire, while a pair of stars (Sadal Bari and Lambda (just southwest of Scheat) were one of the managers arguing with the third-base ump!
Cosmic melodrama
Like several other constellations, Pegasus represents a mythical beast. He is part of the supporting cast of characters involved in an oft-told celestial soap opera that includes King Cepheus, Queen Cassiopeia, princess Andromeda, Perseus the Hero and Cetus the Sea Monster. All are also favorably placed for viewing in our November evening sky.
According to the story, Andromeda was chained to a rock as Cetus approached to devour her. Perseus happened to be riding high in the sky on Pegasus, and, when he saw what was about to happen, he pulled from his bag the head of the gorgon Medusa. He held the head in front of Cetus, which promptly turned him into stone. Perseus then carried off his bride-to-be on Pegasus, and they all lived happily ever after.
Most astronomy books provide various versions of this story, and yet, rarely is Pegasus ever mentioned in Perseus’ other adventures.
A sad end for an egomaniac
On another occasion, a youth by the name of Bellerophon was tasked with destroying a fire-breathing monster known as the Chimera, which had a lion’s head, a goat’s body and a dragon’s tail.
Bellerophon spent an entire night in the temple of the goddess Minerva, imploring her to help him carry out his task. The next morning, Bellerophon awoke and found a golden bridle in his hand and Pegasus drinking from a nearby fountain. With the aid of his new equine friend, Bellerophon dispatched the Chimera with relative ease; in fact, Pegasus seemed to give him godlike powers, and the young man soon began to regard himself as more than just an ordinary mortal.
Bellerophon ultimately decided to visit Mount Olympus, the home of the gods, which was strictly off-limits to mortals. As horse and rider approached the Olympian gates, Zeus sent a gadfly to sting Pegasus, who bolted and threw his rider. When Bellerophon crashed back to Earth, he was rendered blind and lame for the rest of his life.
A nonmythological footnote involves Napoleon Bonaparte, the real-life military commander who at the height of his power perhaps thought that he too was more than mortal. After a French army under his command was defeated at the Battle of Waterloo in June 1815, Napoleon boarded a ship of the British Royal Navy so he could surrender to the ship’s captain, thus ending 22 years of almost continuous war between Britain and France.
The name of that ship was the HMS Bellerophon<em>.
Joe Rao serves as an instructor and guest lecturer at New York’s Hayden Planetarium. He writes about astronomy for Natural History magazine, Sky and Telescope and other publications.
